When it comes to estate planning, most people are familiar with written wills that outline how their assets should be distributed after their death. However, there are different types of wills, including the lesser-known nuncupative will. Understanding what a nuncupative will is and its legal standing can help you make informed decisions about your estate planning needs. Here’s a comprehensive look at nuncupative wills.
Definition of a Nuncupative Will
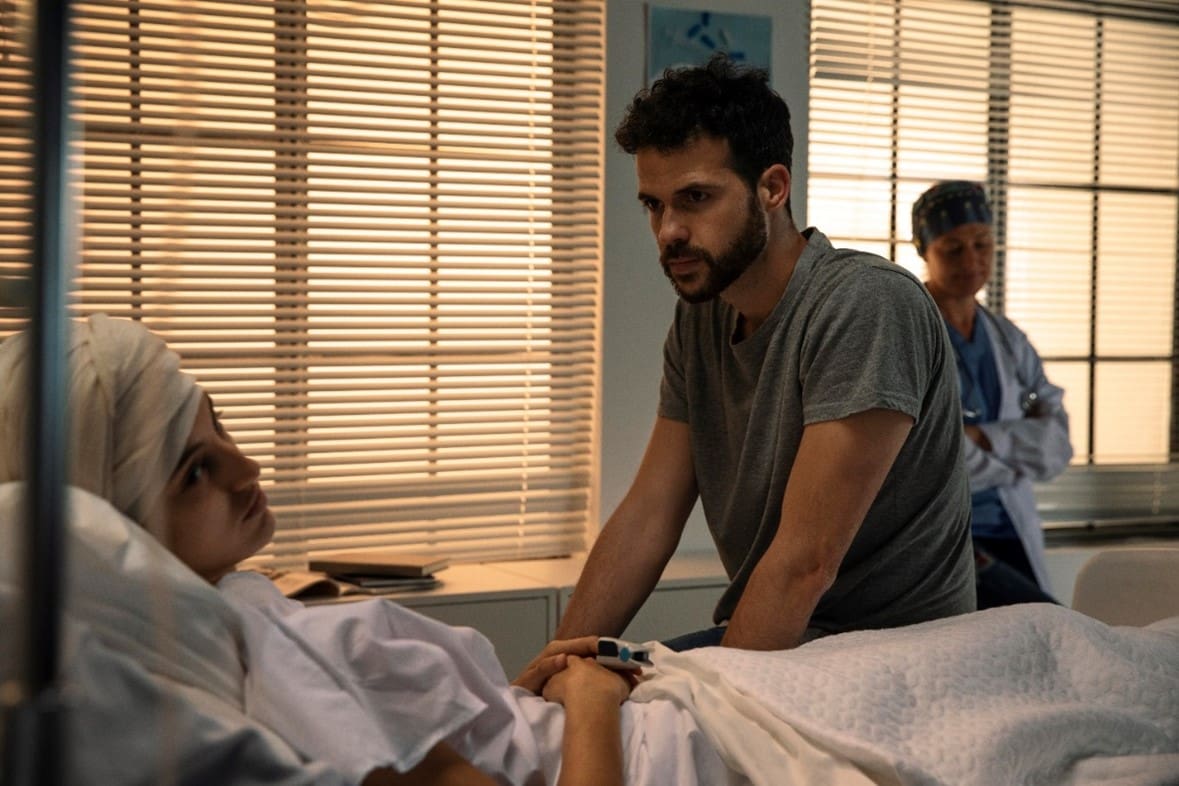
A nuncupative will, commonly known as an oral or verbal will, is a will that is spoken rather than written. These wills are typically made in emergency situations, such as when a person is facing imminent death and cannot draft a written will. The nuncupative will is declared aloud to witnesses, who later document the deceased’s wishes.
Key Characteristics of Nuncupative Wills
-
Verbal Declaration:
- Unlike traditional wills, which are documented in writing, a nuncupative will is declared verbally by the testator (the person making the will).
-
Witness Requirement:
- Nuncupative wills require the presence of witnesses who hear the testator’s declarations. The number of witnesses required can vary by jurisdiction, but typically at least two witnesses are needed.
-
Limited Acceptance:
- Nuncupative wills are not universally accepted and are only recognized under specific circumstances and in certain jurisdictions. They are generally considered less reliable than written wills due to the potential for miscommunication and lack of formal documentation.
-
Emergency Situations:
- These wills are usually made in emergency situations where the testator is facing imminent death and does not have the opportunity to create a written will. Common scenarios include sudden illness or injury.
-
Scope and Limitations:
- The scope of nuncupative wills is often limited to personal property rather than real estate. Some jurisdictions also impose restrictions on the value of the estate that can be disposed of through a nuncupative will.
Legal Requirements and Validity

The validity of a nuncupative will depends on specific legal requirements, which can vary significantly by jurisdiction. Common requirements include:
-
Imminent Death:
- The testator must be in a situation where death is imminent, and there is no time to draft a written will.
-
Witnesses:
- The will must be declared in the presence of a certain number of witnesses who can later attest to the testator’s wishes.
-
Documentation:
- After the testator’s death, the witnesses must promptly document the nuncupative will in writing and submit it to probate court. There may be a time limit for this documentation to be considered valid.
-
Jurisdictional Acceptance:
- Not all states or countries recognize nuncupative wills. Even in jurisdictions that do, the acceptance of such wills is typically limited and subject to strict scrutiny.
Advantages of Nuncupative Wills
-
Quick and Immediate:
- In situations where time is of the essence, a nuncupative will allows individuals to express their last wishes without the need for formal documentation.
-
Flexibility:
- They provide a flexible option for those who may not have a written will in place but want to ensure their personal property is distributed according to their wishes.
Disadvantages of Nuncupative Wills
-
Legal Uncertainty:
- The lack of formal documentation and the reliance on witnesses can lead to disputes and legal challenges, making nuncupative wills less reliable than written wills.
-
Limited Recognition:
- The validity of nuncupative wills is limited to specific jurisdictions and circumstances, and they are not universally accepted.
-
Potential for Miscommunication:
- The verbal nature of these wills increases the risk of miscommunication or misinterpretation of the testator’s wishes.
If you have feedback, questions, or ideas for future articles or Information Hubs, please contact us. Your insights help us create valuable content.